An Optimal Algorithm for the Stacker Crane Problem on Fixed Topologies
Stacker Crane on a graph
\(\newcommand{\R}{\mathbb{R}}\) \(\newcommand{\Z}{\mathbb{Z}}\) \(\newcommand{\N}{\mathbb{N}}\)
For a graph \(G=(V,E)\) with cost on the edges. A single vehicle with capacity 1 is at position \(s_0\in V\).
- There are \(p\) requests of the form \((s_i,t_i) \in R \subseteq V\times V\).
- Complete a request: vehicle pick up item \(i\) from \(s_i\), and move it to \(t_i\) without dropping it off anywhere on the way.
- Goal: Find a tour that start and end on \(s_0\), completes all requests and minimizes the total cost.
Stacker Crane on a path
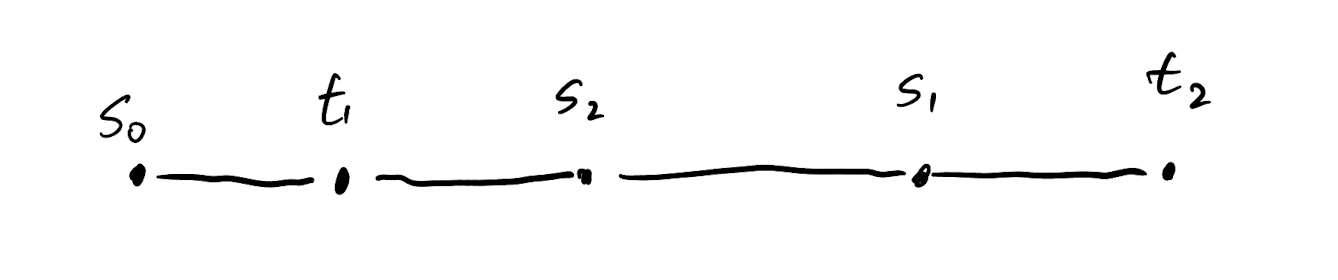
Stacker Crane on a path
\(s_0\)
\(\color{blue}{s_1}\)
\(\color{blue}{t_1}\)
\(\color{red}{s_2}\)
\(\color{red}{t_2}\)
Stacker Crane on a path
\(s_0\)
\(\color{blue}{s_1}\)
\(\color{blue}{t_1}\)
\(\color{red}{s_2}\)
\(\color{red}{t_2}\)
Stacker Crane on a path
\(s_0\)
\(\color{blue}{s_1}\)
\(\color{blue}{t_1}\)
\(\color{red}{s_2}\)
\(\color{red}{t_2}\)
Stacker Crane on a path
\(s_0\)
\(\color{blue}{s_1}\)
\(\color{blue}{t_1}\)
\(\color{red}{s_2}\)
\(\color{red}{t_2}\)
Stacker Crane on a path
\(s_0\)
\(\color{blue}{s_1}\)
\(\color{blue}{t_1}\)
\(\color{red}{s_2}\)
\(\color{red}{t_2}\)
Stacker Crane on a path
\(s_0\)
\(\color{blue}{s_1}\)
\(\color{blue}{t_1}\)
\(\color{red}{s_2}\)
\(\color{red}{t_2}\)
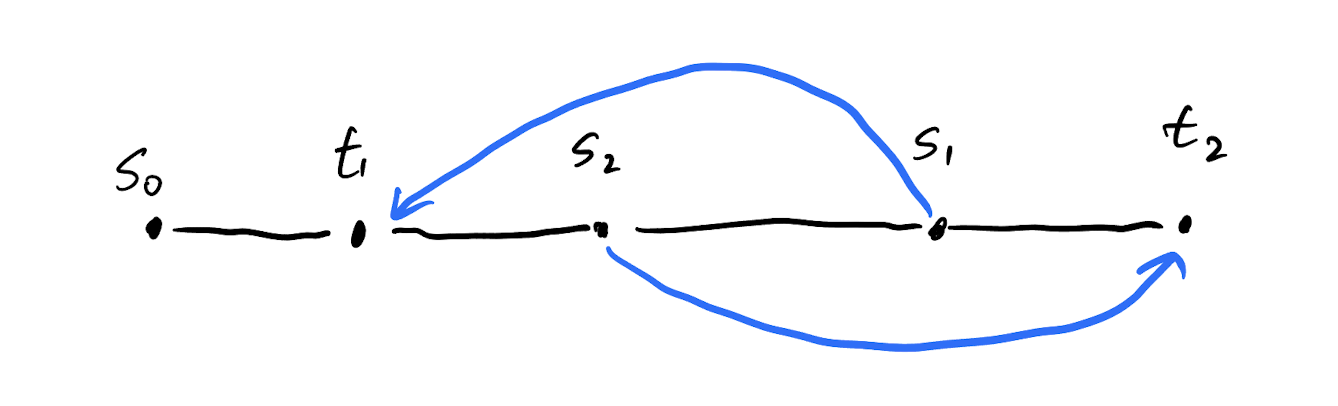
Stacker Crane on a path (Not as good)
\(s_0\)
\(\color{blue}{s_1}\)
\(\color{blue}{t_1}\)
\(\color{red}{s_2}\)
\(\color{red}{t_2}\)
Mixed Graph Formulation
Input: A base graph \(B=(V,E)\), requests \(R\subseteq V\times V\), cost \(c:E\to \R^+\). Let \(G=(V,E\cup R)\) be a mixed graph.
Output: A min-cost tour of \(G\) where each edge in \(R\) is used exactly once.
\(m=|E|\), \(n=|V|\), \(p=|R|\)
Stacker Crane Extensions
Generalizations are called dial-a-ride problems.
- Online (Lois and Ziliaskopoulos 2017; Baligács et al. 2022)
- Multiple Vehicles (Desrosiers, Dumas, and Soumis 1988)
- Capacities (Charikar and Raghavachari 1998)
- Time windows (Deleplanque and Quilliot 2013)
- Preemptive (Gørtz 2006)
- Approximation algorithms. (Frederickson, Hecht, and Kim 1978; Charikar and Raghavachari 1998; Sun, Yu, and Liu 2022; Li et al. 2017; Yu, Dai, and Liu 2023)
- …
Known results
For base graphs:
- Path \(-\): \(O(MST(m)+p)\) time. (Atallah and Kosaraju 1988) \(\Omega(MST(m))\) time lower bound. (Frederickson 1993)
- Cycle \(\bigcirc\): \(O(MST(m)+p)\) time. (Frederickson 1993)
- Trees: NP-hard! (Frederickson and Guan 1993)
- \(\boxminus\) shape: Unknown
- \(\top\) shape: Unknown
Motivation: Topology of Warehouses
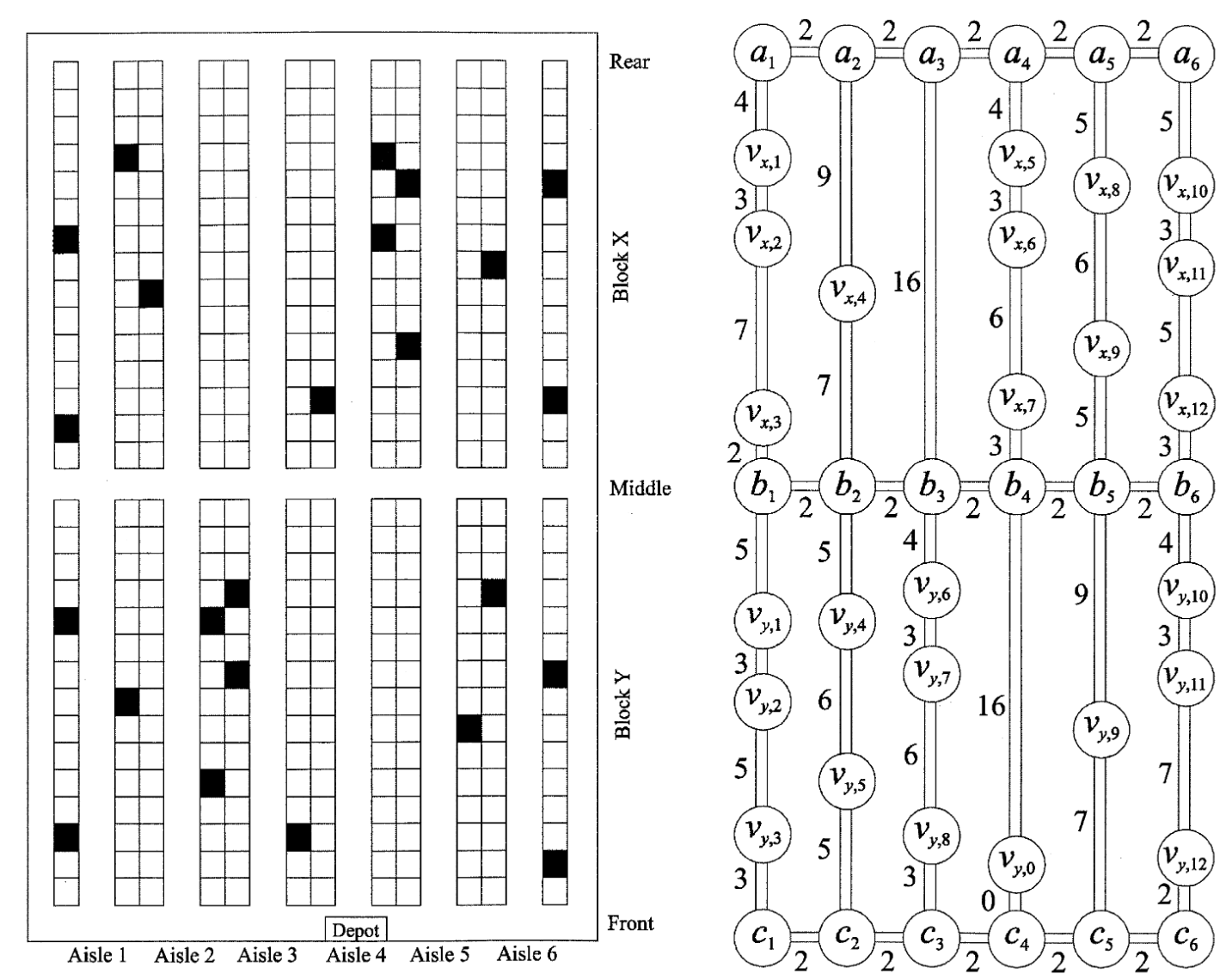
Image courtesy (Roodbergen and Koster 2001)
Our result
Stacker Crane Problem for a fixed topology can be solved in \(O(MST(m)+p)\) time.
Stacker Crane Problem is FPT parametrized by cycle rank and branch number of the base graph.
In This talk
- Review the algorithm for paths and cycles
- Show the correct generalization to general graphs
Solve SCP on paths and cycles
Algorithms of (Atallah and Kosaraju 1988; Frederickson 1993).
Tours and flows
Using the original formulation (no mixed graph).
- Every solution (tour) maps to a circulation: the difference of the tour edge going forward and backwards is the flow on the edge.
Paths
Tour traverse through a edge forward and backward the same number of times. Flow is \(0\) on all edges (flow condition).
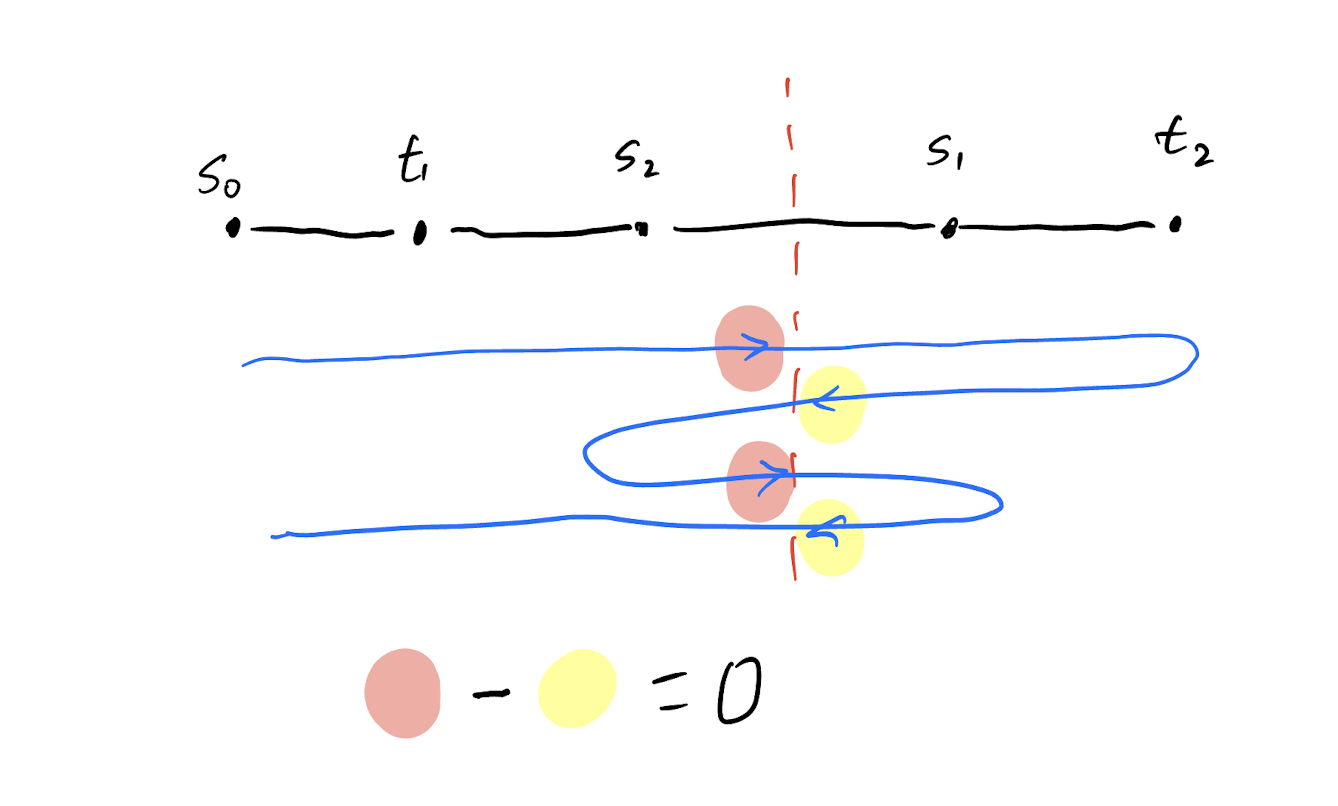
The tour must traverse through \(s_i\) to \(t_i\).
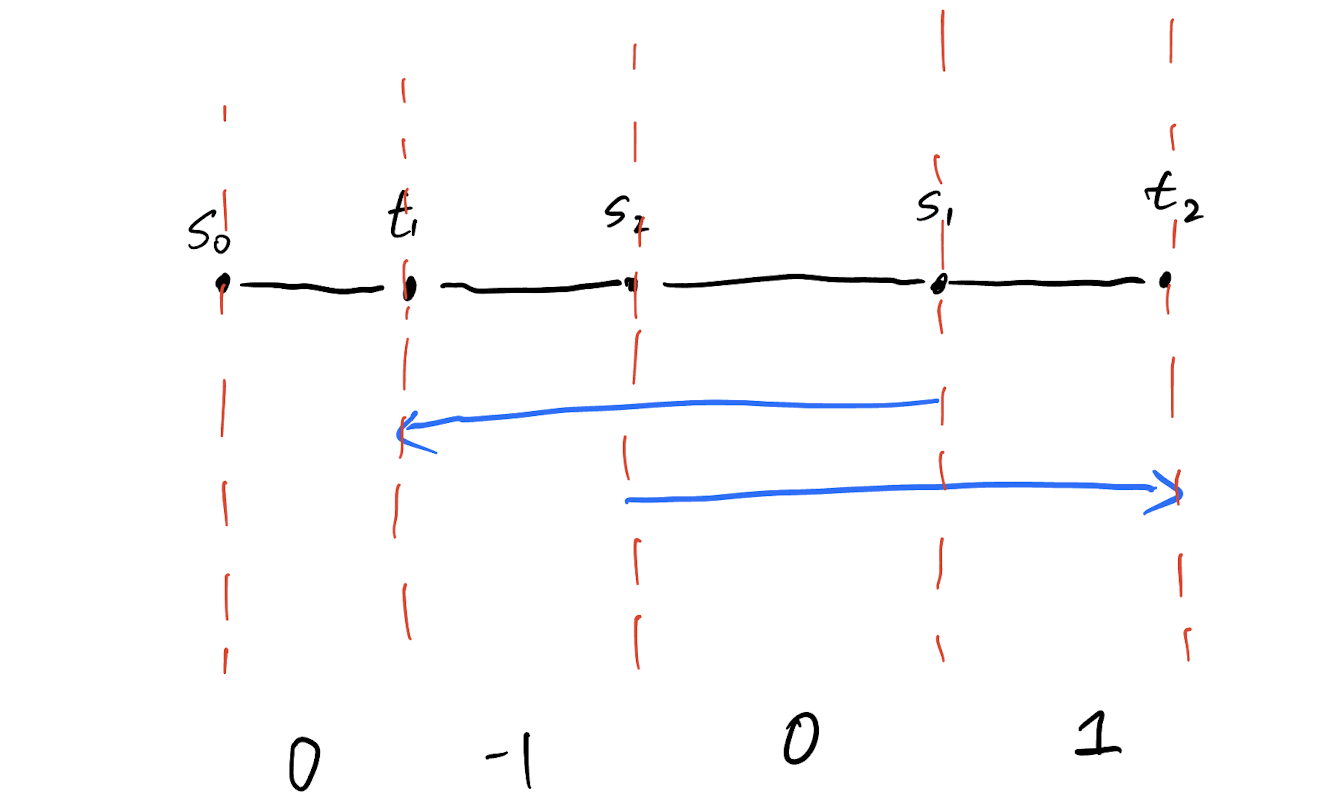
Add paths to fix the flow condition.
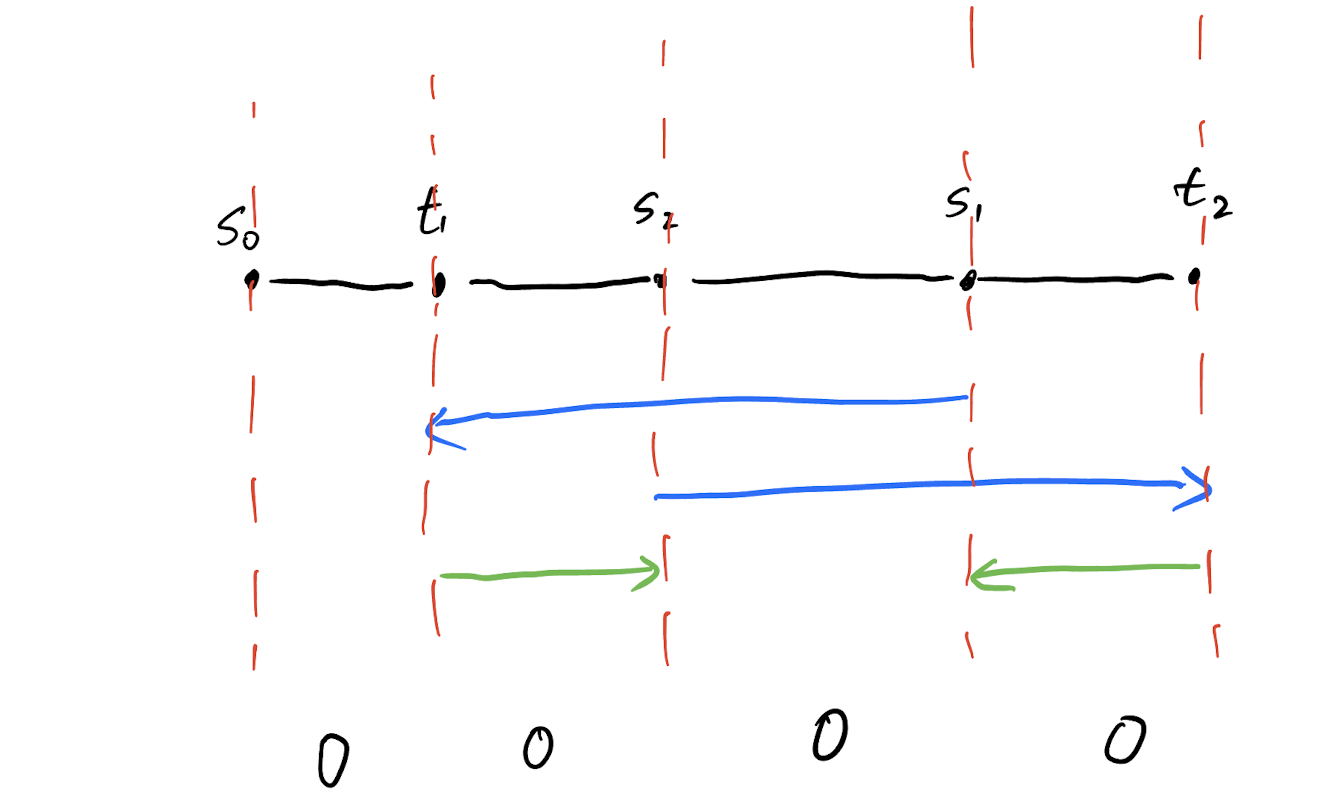
Add opposing edges to make sure the tour is connected.
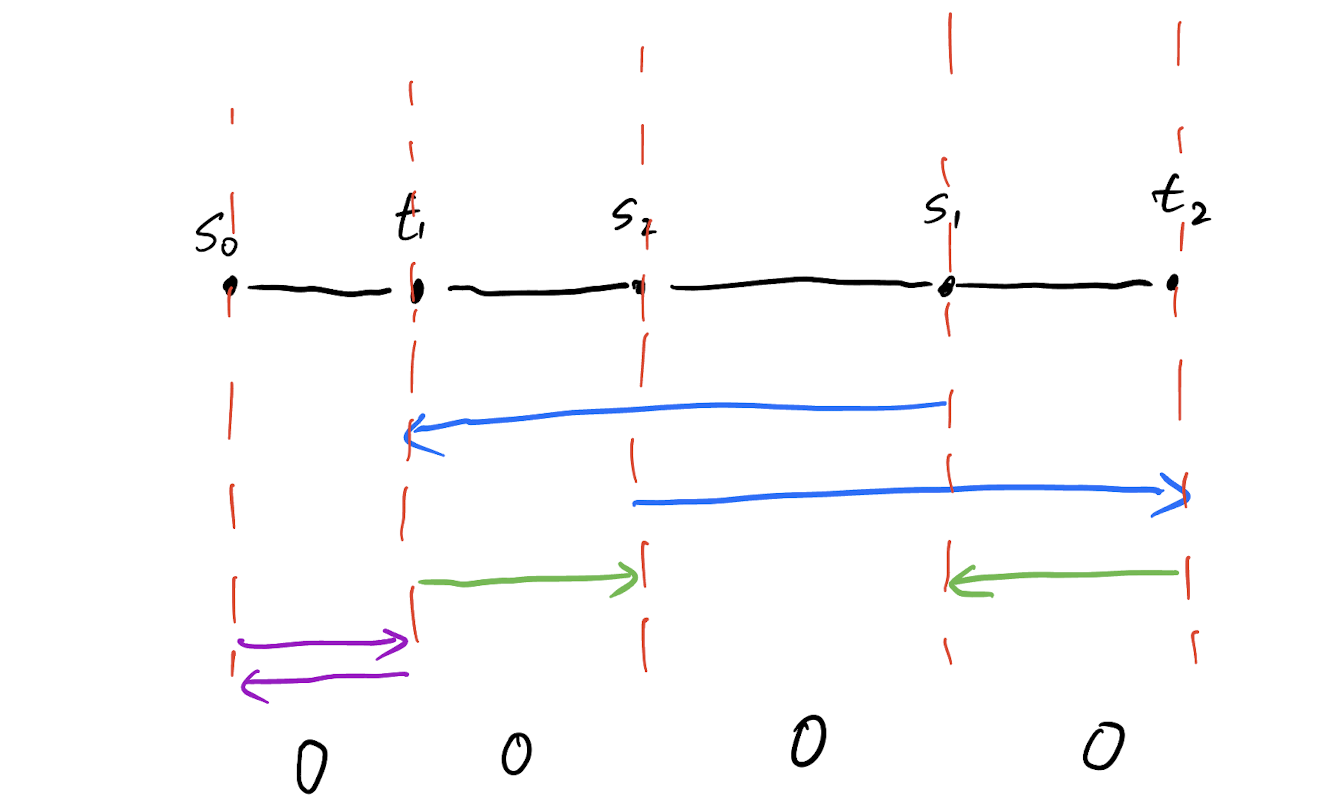
Remove some vertices not incident to any edge already in the tour.
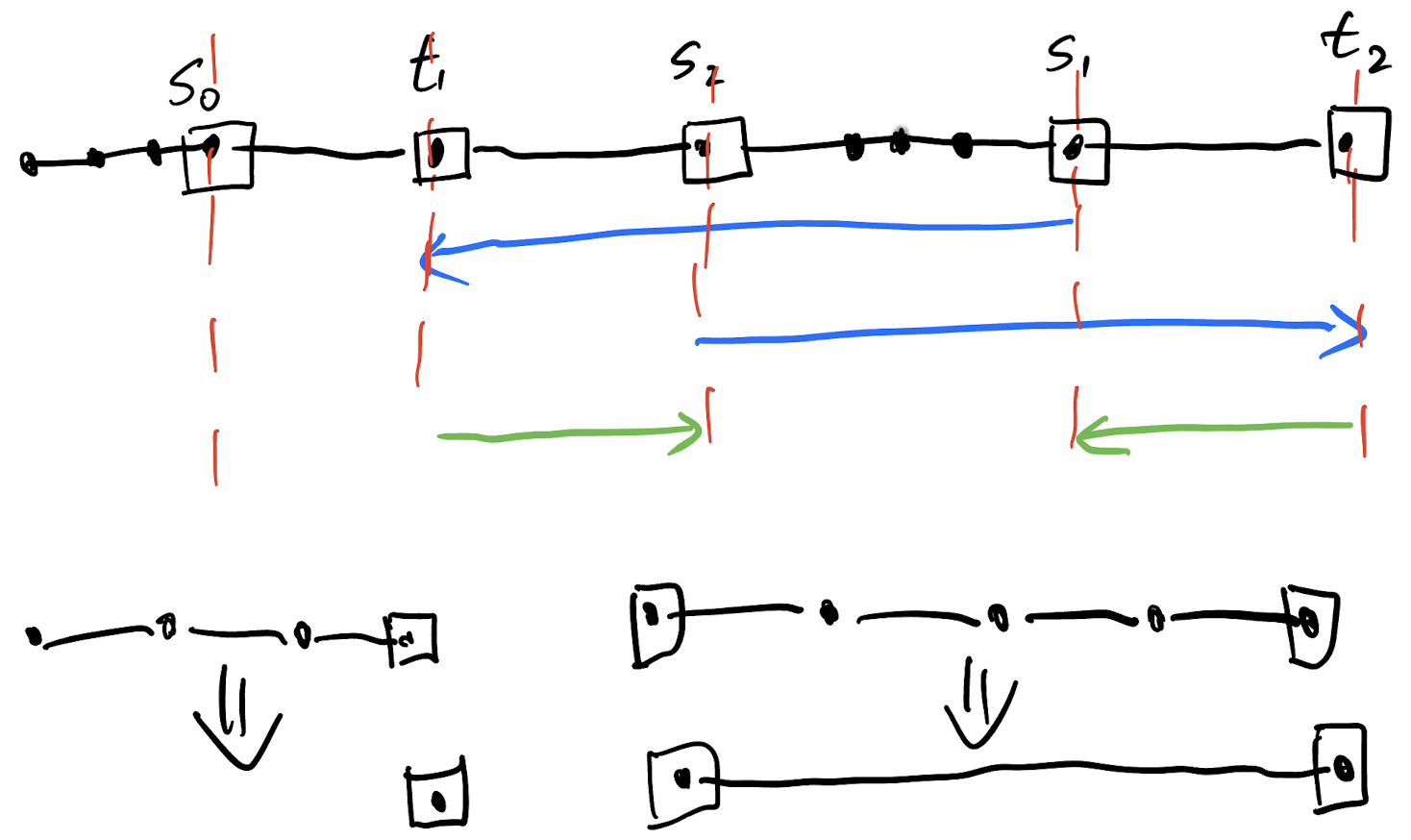
Reduced to minimum spanning tree.
Obtain a complete solution by construct a tour through the chosen edges.
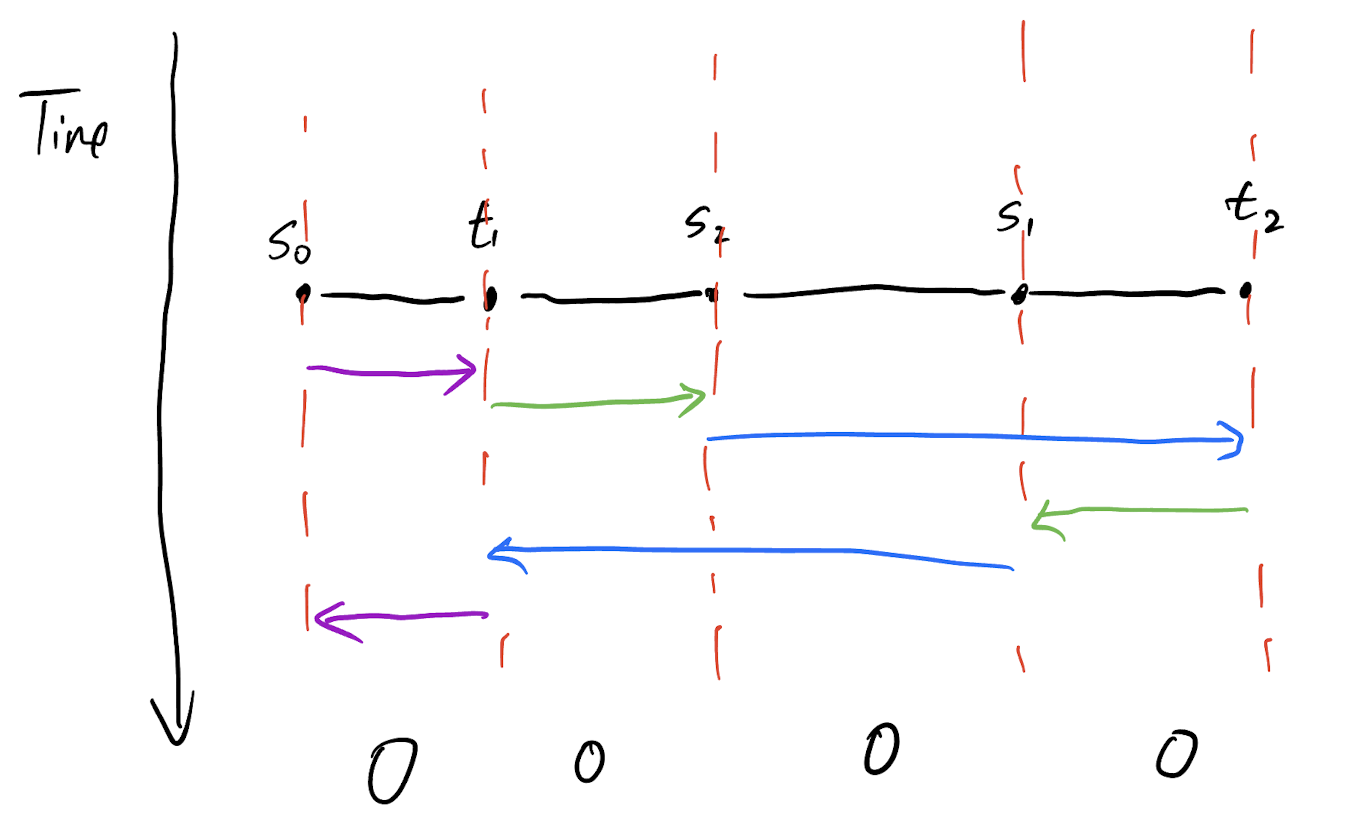
SCP on a cycle
flow = 0?
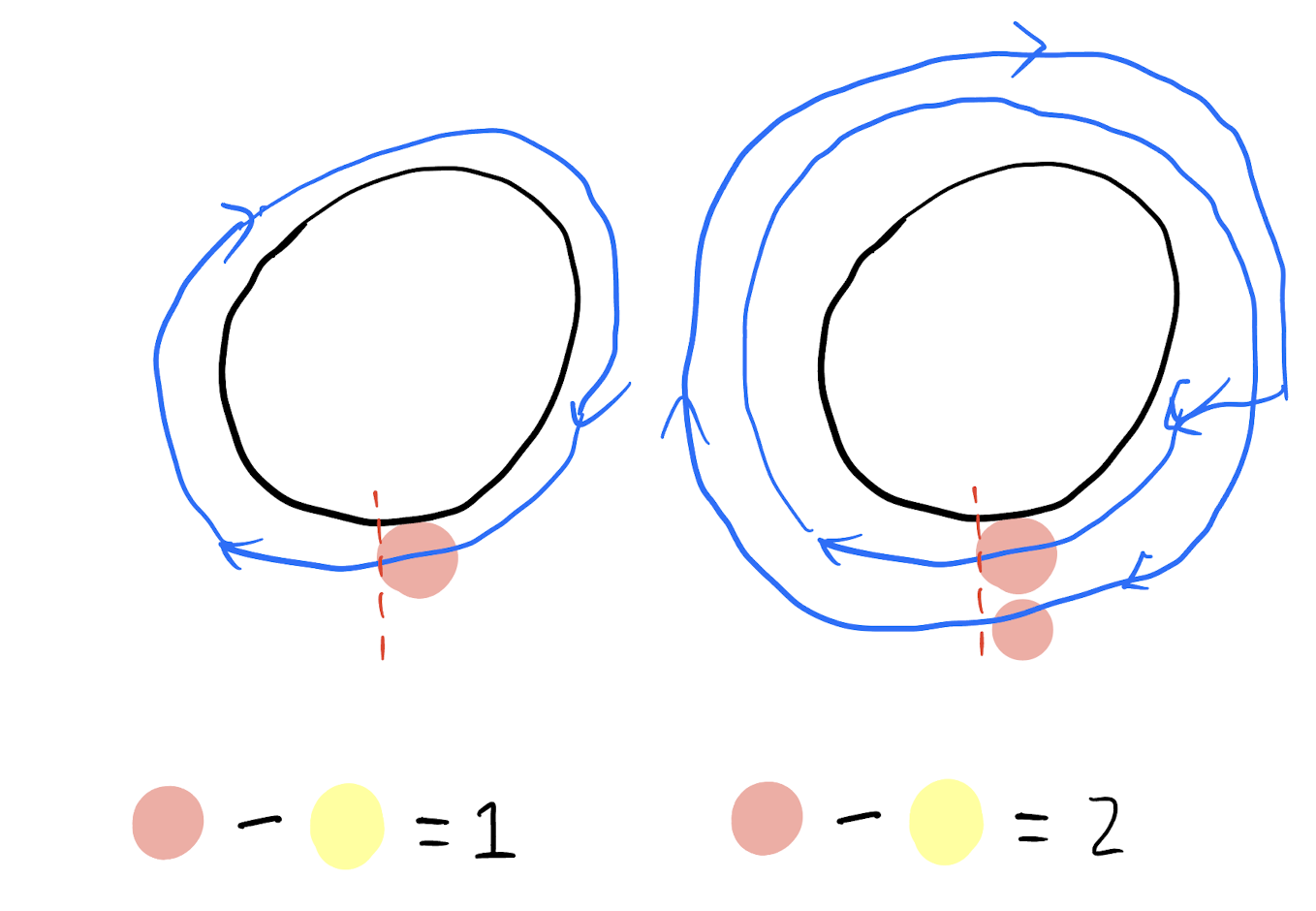
Winding Number
- The flow is equal on each edge! (the new flow condition)
- The winding number.
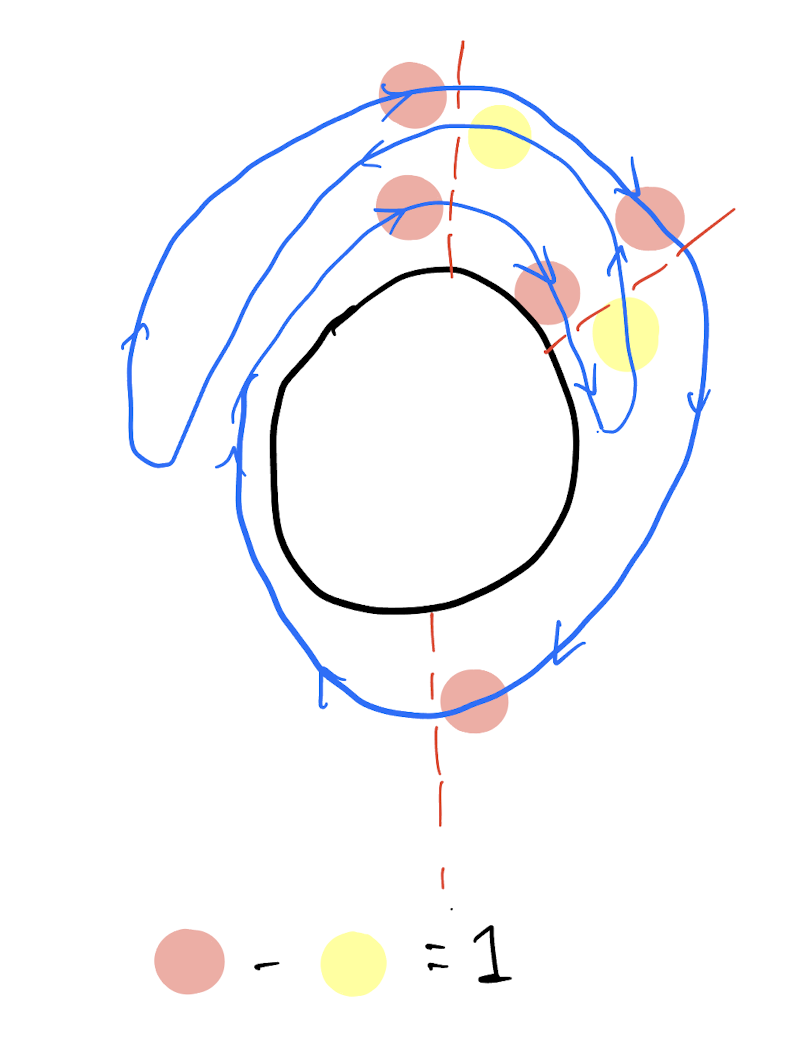
Solution with winding number = 1
First, add the request paths.
Solution with winding number = 1
Add edges to make sure each edge forward - backword = 1
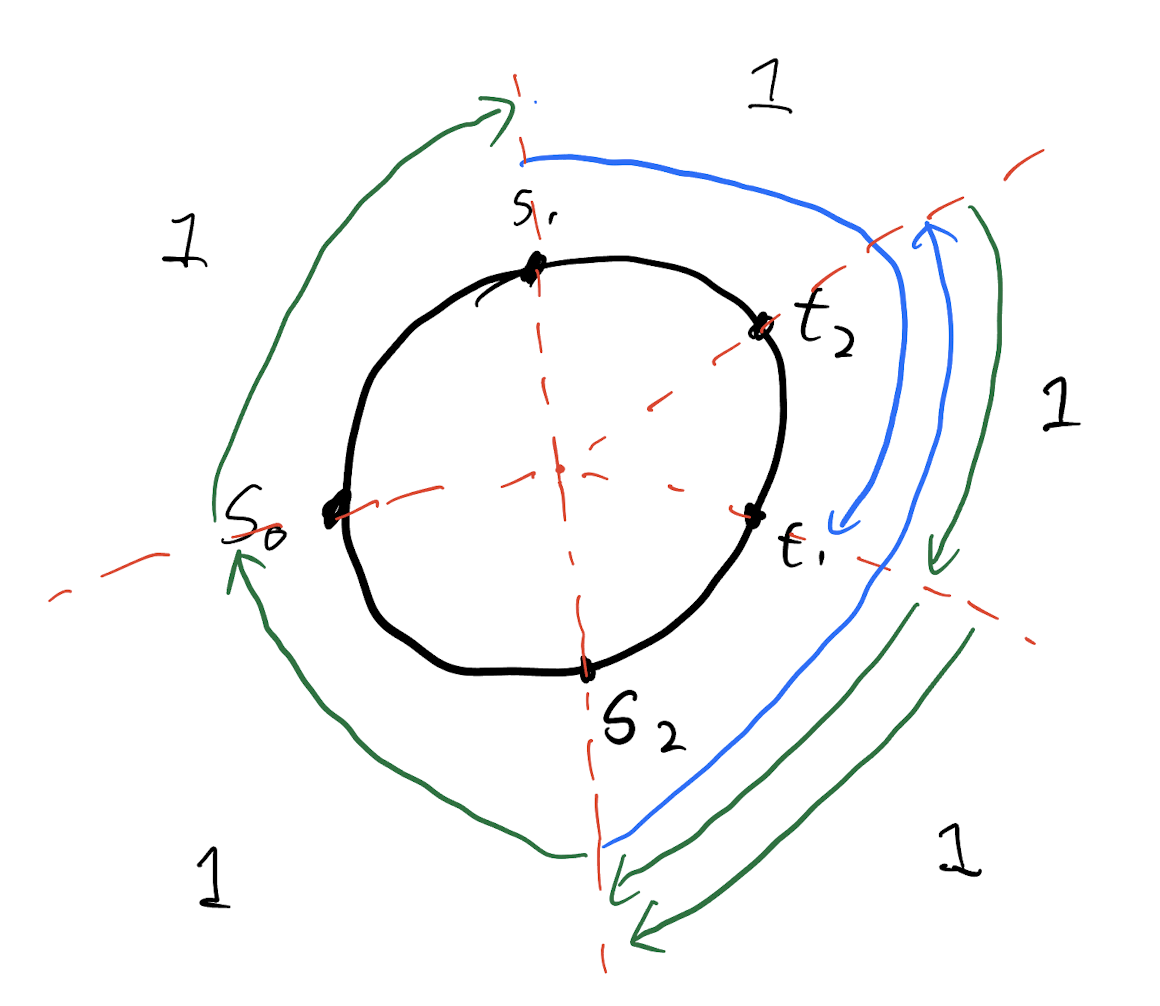
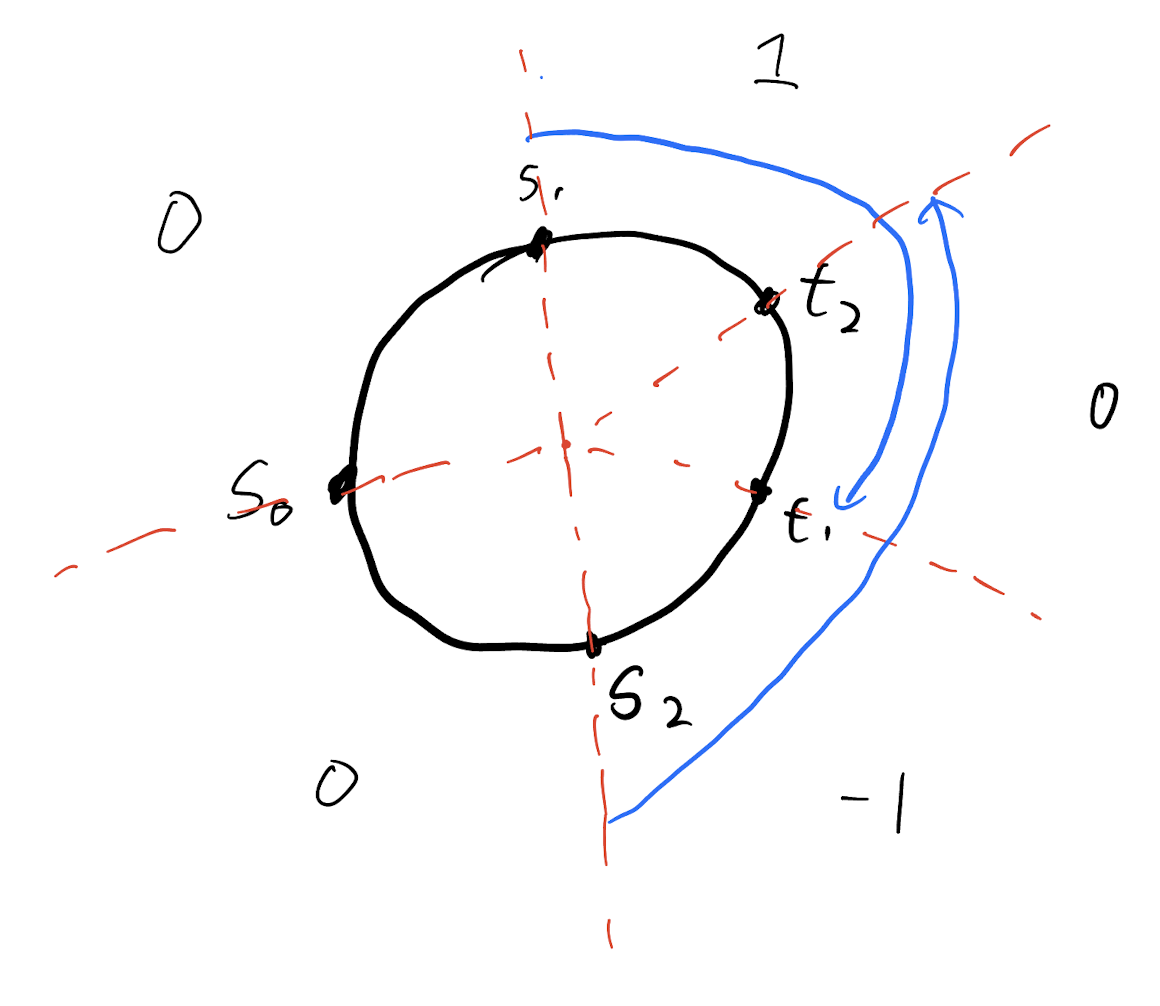
Solution with winding number = 1
Run minimum Steiner tree to get the set opposing edges to connect the tour.

A complete solution for cycles
- Guess all possible winding numbers.
- The guess is in between \([-p,p]\).
- For each guess \(w\), compute a optimum solution with winding number \(w\).
- \(O(p(MST(m)+p))\) running time.
Proximity Result
- Find a min-cost circulation \(f\) that satisfies the flow condition.
- Assume the optimum tour maps to circulation \(g\).
- \(\|f-g\|_\infty \leq 1\) (Frederickson 1993)
- \(O(MST(m)+p)\) running time.
SCP on general graphs
Min-cost tour
- Think in mixed graph formulation.
- A valid circulation \(f\), is a circulation with flow value \(f(e)=1\) on each edge \(e\in R\). All circulations are valid circulations from this point on.
- Each tour maps to a circulation. \([f]:=\) tours that maps to \(f\).
- \([f]\) is called a homology class.
- \(r:=m-n+1\) is the cycle rank of the base graph \(B\).
- Vertices with degree \(\geq 3\) are branch vertices.
- \(k\) is the number of branch vertices in \(B\).
Interpertation of the algorithm
- Find a min-cost circulation \(f\).
- Find all circulations \(g\) such that \(\|f-g\|_\infty\leq r\).
- Find a min-cost tour in each \([g]\) and returns the minimum.
Proximity Theorem
Let \(f\) be the min-cost circulation, the min-cost tour is in \([g]\) for some circulation \(g\) such that \(\|f-g\|_\infty\leq r\).
Min-cost circulation
- Reduces to min-cost flow on tree with \(r\) more edges.
- Reduces to a special kind of linear program.
- The minimizer can be found in \(2^{O(2^r)} m = O(m)\) time (Zemel 1984).
Enumerate circulations
Theorem
There are \(O((2d+1)^r)\) circulations \(g\) such that \(\|f-g\|_\infty \leq d\), and can be enumerated in \(O((2d+1)^rm)\) time.
Minimum Steiner Tree Problem
Minimum Steiner Tree
Given a weighted graph \(G=(V,E)\) and a set of terminal vertices \(T\subseteq V\). Find a minimum weight tree that connects all vertices in \(T\).
- NP-hard in general
- \(O(2^k MST(m))\) time if the input has at most \(k\) Steiner branch vertices.
Min-cost tour in \([g]\)
- \(B'\) obtained from \(G\) by contract all support edges in \(g\).
- \(T\) be all vertices in \(B'\) obtained from contraction.
- min-cost tour in \([g]\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) minimum Steiner tree in \(B'\) with terminals \(T\).
- \(B'\) can have MANY branch vertices, but at most \(k\) Steiner branch vertices.
- Finding min-cost tour in \([g]\) takes \(O(2^k MST(m))\) time.
Results
For a base graph with at most \(k\) branch vertices and cycle rank \(r\), the running time of the SCP algorithm is \(2^{O(2^r)}m + O((2r+1)^{r} 2^k (MST(m) + p))\).
SCP problem for fixed topologies can be solved in \(O(MST(m) + p)\) time.
Open problem
- Min-cost flow on a tree with \(r\) additional edges: Better than \(2^{O(2^r)}m\) time?
- Proximity result: smaller search space than \((2r+1)^r\)?
Open problem
FPT algorithm parametrized by number of branch vertices?
Arbitrary cycle rank, exactly \(1\) branch vertex
